Cost-effective and customizable Glyceryl monostearate 31566-31-1 for sale
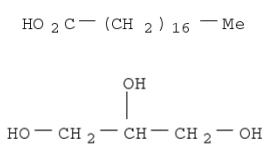
- Molecular Formula:C21H42O4
- Molecular Weight:358.63
- Appearance/Colour:White to creamish flakes / beads
- Melting Point:78-81°C
- Refractive Index:1.4400 (estimate)
- Boiling Point:476.9oC at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:151.9oC
- PSA:66.76000
- Density:0.958 g/cm3
- LogP:5.14430
Glyceryl monostearate(Cas 31566-31-1) Usage
|
Definition
|
An intermediate chemical. |
|
Production Methods
|
Glyceryl monostearate is prepared by the reaction of glycerin with
triglycerides from animal or vegetable sources, producing a mixture
of monoglycerides and diglycerides. The diglycerides may be further
reacted to produce the 90% monoglyceride grade. Another process
involves reaction of glycerol with stearoyl chloride.
The starting materials are not pure substances and therefore the
products obtained from the processes contain a mixture of esters,
including palmitate and oleate. Consequently, the composition, and
therefore the physical properties, of glyceryl monostearate may vary
considerably depending on the manufacturer. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications
|
The many varieties of glyceryl monostearate are used as nonionic
emulsifiers, stabilizers, emollients, and plasticizers in a variety of
food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications. It acts as an
effective stabilizer, that is, as a mutual solvent for polar and
nonpolar compounds that may form water-in-oil or oil-in-water
emulsions.These properties also make it useful as a dispersing
agent for pigments in oils or solids in fats, or as a solvent for
phospholipids, such as lecithin.
Glyceryl monostearate has also been used in a novel fluidized
hot-melt granulation technique for the production of granules and
tablets.
Glyceryl monostearate is a lubricant for tablet manufacturing
and may be used to form sustained-release matrices for solid dosage
forms. Sustained-release applications include the formulation of
pellets for tablets or suppositories, and the preparation of a
veterinary bolus. Glyceryl monostearate has also been used as a
matrix ingredient for a biodegradable, implantable, controlledrelease
dosage form.
When using glyceryl monostearate in a formulation, the
possibility of polymorph formation should be considered. The aform
is dispersible and foamy, useful as an emulsifying agent or
preservative. The denser, more stable, b-form is suitable for wax
matrices. This application has been used to mask the flavor of
clarithromycin in a pediatric formulation. |
|
Safety Profile
|
Poison by
intraperitoneal route. When heated to
decomposition it emits acrid smoke and
irritating fumes. See also ESTERS. |
|
Safety
|
Glyceryl monostearate is widely used in cosmetics, foods, and oral
and topical pharmaceutical formulations, and is generally regarded
as a nontoxic and nonirritant material.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.2 g/kg |
|
storage
|
If stored at warm temperatures, glyceryl monostearate increases in
acid value upon aging owing to the saponification of the ester with
trace amounts of water. Effective antioxidants may be added, such
as butylated hydroxytoluene and propyl gallate.
Glyceryl monostearate should be stored in a tightly closed
container in a cool, dry place, and protected from light. |
|
Incompatibilities
|
The self-emulsifying grades of glyceryl monostearate are incompatible
with acidic substances. |
|
Regulatory Status
|
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database
(oral capsules and tablets; ophthalmic, otic, rectal, topical,
transdermal, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral
medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of
Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
If glyceryl monostearate is produced from animal fats (tallow),
there may be additional regulatory requirements that the source be
free of contamination from bovine spongiform encephalopathy. |
InChI:InChI=1/2C21H42O4/c2*1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-21(24)25-20(18-22)19-23/h2*20,22-23H,2-19H2,1H3